Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context, and Africa has a large quantity of natural resources.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa is also heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them "oral civilisations", contrasted with "literate civilisations" which pride the written word. African culture is rich and diverse both within and between the continent's regions, encompassing art, cuisine, music and dance, religion, and dress.
Africa, particularly Eastern Africa, is widely accepted to be the place of origin of humans and the Hominidae clade, also known as the great apes. The earliest hominids and their ancestors have been dated to around 7 million years ago, and Homo sapiens (modern human) are believed to have originated in Africa 350,000 to 260,000 years ago. In the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE Ancient Egypt, Kerma, Punt, and the Tichitt Tradition emerged in North, East and West Africa, while from 3000 BCE to 500 CE the Bantu expansion swept from modern-day Cameroon through Central, East, and Southern Africa, displacing or absorbing groups such as the Khoisan and Pygmies. Some African empires include Wagadu, Mali, Songhai, Sokoto, Ife, Benin, Asante, the Fatimids, Almoravids, Almohads, Ayyubids, Mamluks, Kongo, Mwene Muji, Luba, Lunda, Kitara, Aksum, Ethiopia, Adal, Ajuran, Kilwa, Sakalava, Imerina, Maravi, Mutapa, Rozvi, Mthwakazi, and Zulu. Despite the predominance of states, many societies were heterarchical and stateless. Slave trades created various diasporas, especially in the Americas. From the late 19th century to early 20th century, driven by the Second Industrial Revolution, most of Africa was rapidly conquered and colonised by European nations, save for Ethiopia and Liberia. European rule had significant impacts on Africa's societies, and colonies were maintained for the purpose of economic exploitation and extraction of natural resources. Most present states emerged from a process of decolonisation following World War II, and established the Organisation of African Unity in 1963, the predecessor to the African Union. The nascent countries decided to keep their colonial borders, with traditional power structures used in governance to varying degrees. (Full article...)
Selected article –
The Egyptian–Libyan War, also known as the Four Day War (Arabic: حرب الأربعة أيام, romanized: ḥarb al-ārbaʿ ʾayyām), was a short border war fought between Libya and Egypt that lasted from 21 to 24 July 1977. The conflict stemmed from a deterioration in relations that had occurred between the two states after Egyptian President Anwar Sadat had rebuffed Libyan leader Muammar Gaddafi's entreaties to unify their countries and had pursued a peace settlement with Israel in the aftermath of the Yom Kippur War in 1973. Soon thereafter Libya began sponsoring dissidents and assassination plots to undermine Sadat, and Egypt responded in kind to weaken Gaddafi. In early 1976 Gaddafi dispatched troops to the Egyptian frontier where they began clashing with border guards. Sadat responded by moving many troops to the area, while the Egyptian General Staff drew up plans for an invasion to depose Gaddafi.
Clashes along the border intensified in July 1977. On 21 July a Libyan tank battalion raided the town of Sallum. The Egyptian forces ambushed it and subsequently launched a large counter-attack, conducting airstrikes against Gamal Abdel Nasser Airbase and sending a mechanised force 24 kilometres (15 mi) into Libyan territory before withdrawing. Over the next two days, heavy artillery fire was exchanged across the border, while Egyptian jets and commandos raided Libyan locales. On 24 July the Egyptians launched a larger raid against Nasser Airbase and struck Libyan supply depots. Under significant pressure from the United States to end the attacks, and attempts from President of Algeria Houari Boumediène and Palestine Liberation Organisation leader Yasser Arafat to mediate a solution, Sadat suddenly declared a ceasefire. Sporadic fighting occurred over the next few days as Egyptian troops withdrew across the border. Relations between the two countries remained tense, and, though a formal agreement was never reached, both upheld a truce and gradually withdrew their forces from the border. Gaddafi softened his rhetoric against Egypt in the following years but actively rallied other Arab states to isolate the country. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Louise Fulton was the first African American to win a professional bowling tournament?
- ... that Pocatello mayor Les Purce was the first African-American political officeholder in Idaho?
- ... that after Benjamin Moloise's execution, the extremist group Direct Action bombed two Paris companies linked to South Africa in protest?
- ... that scientists tested the age of an African termite's inhabited mound—and found it to be 34,000 years old?
- ... that in 1948, Thomas Yarborough became the first African American to be elected as a city council member in California?
- ... that Gil Scott-Heron's 1975 song "Johannesburg" was banned in South Africa during apartheid?
Categories
Selected biography –

Dedan Kimathi Waciuri (born Kimathi wa Waciuri; 31 October 1920 – 18 February 1957) was the leader of the Kenya Land and Freedom Army during the Mau Mau Uprising (1952–1960) against the British colonial rule in Kenya in the 1950s. He was captured by the British in 1956 and executed in 1957. Kenya gained independence in 1963. Kimathi is credited with leading efforts to create formal military structures within the Mau Mau, and convening a war council in 1953. He, along with Baimungi M'marete, Musa Mwariama, Kubu Kubu, General China and Muthoni Kirima, was one of the Field Marshals.
Kenyan nationalists view him as a freedom fighter in the Kenyan struggle for independence, while the British colonial authorities saw Kimathi as a terrorist, and according to historian David Anderson "did all they could to besmirch his reputation." Despite being viewed negatively by Kenya's first two presidents, Jomo Kenyatta and Daniel arap Moi, Kimathi and his fellow Mau Mau rebels were officially recognised as heroes in the struggle for Kenyan independence under the Mwai Kibaki administration, culminating in the unveiling of a Kimathi statue in 2007. This was reinforced by the passage of a new Constitution in 2010 calling for recognition of national heroes. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
||
| |||
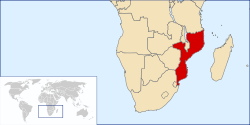
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique (Portuguese: República de Moçambique), is a country in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west and Eswatini and South Africa to the southwest. It was explored by Vasco da Gama in 1498 and colonized by Portugal in 1505.
The north-central provinces of Zambezia and Nampula are the most populous, containing about 45% of the population. The estimated four million Makua are the dominant group in the northern part of the country; the Sena and Shona (mostly Ndau) are prominent in the Zambezi valley, and the Shangaan (Tsonga) dominate in southern Mozambique.
Portuguese is the official and most widely spoken language, spoken by 40% of the population. Most educated Mozambicans speak English, which is used in schools and business as a second or third language. (Read more...)
Selected city –
Windhoek (/ˈwɪndhʊk/; Afrikaans: [ˈvəntɦuk] ⓘ; German: [ˈvɪnthʊk] ⓘ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around 1,700 m (5,600 ft) above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek, was 486,169 in 2023, is constantly growing due to a continued migration from other regions in Namibia.
Windhoek is the social, economic, political, and cultural centre of the country. Nearly every Namibian national enterprise, governmental body, educational and cultural institution is headquartered there. (Full article...)
In the news
- 10 April 2025 – Land reform in Zimbabwe
- Zimbabwe begins issuing the first financial compensation payments to White Zimbabwean farmers whose farms were seized by Robert Mugabe's government between 2000 and 2002. A total of 740 farmers will be compensated as per the 2020 agreement with the Commercial Farmers' Union. (BBC News)
- 8 April 2025 –
- The death toll from the heavy flooding in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo, caused by overflow of the Ndjili River increases to 33 deaths. Hundreds of buildings are completely submerged and thousands of people are trapped in their homes. (NPR) (DW)
- About 50 hippos are killed by anthrax poisoning at Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. (CTV News)
- 8 April 2025 – 2024 Democratic Republic of the Congo coup attempt, Democratic Republic of the Congo–United States relations
- Three U.S. citizens have their sentences for attempting a coup against the Congolese President Félix Tshisekedi in 2024 commuted and are extradited back to the United States. They were previously sentenced to death along with 34 others for the failed attempt that killed six people, including the coup's leader Christian Malanga. (NPR)
- 7 April 2025 – Herder–farmer conflicts in Nigeria
- The National Emergency Management Agency reports that at least 52 people have been killed and over 2,000 others have been displaced from their homes in recent days in tit for tat attacks by rival herders over control of arable land in Plateau State, Nigeria. (Reuters)
- 7 April 2025 – Algeria–Mali relations
- Algeria bans flights to and from Mali in response to "recurrent violations" of Algerian airspace by Malian military drones. (Reuters)
Updated: 11:05, 12 April 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ...that members of the Senegalese rap group Daara J were hired by campaigners in the Senegalese election of 2000 to edit their speeches?
- ...that Senegalese hip hop group Positive Black Soul's name abbreviation, PBS, is a play on that of the Parti Démocratique Sénégalais, PDS?
- ...that Mamadou Diabaté, a Malian kora player, was nominated for a Grammy Award in 2005, but lost to his cousin Toumani Diabaté?
- ...that, in November 2007, The Sowetan published an article which erroneously claimed that South African political activist Dan Mokonyane had died?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



























































































